- Participates in the construction of membranes and cell walls- ensures the stability of plant structures (bonding of calcium pectinate chains)
- Beneficially affects the hormone balance of plants including the proper division of cells through which it affects the growth of the root system and aboveground shoots
- Increases the resistance of plants to adverse conditions especially drought by strengthening cell wall structures,
- Coordinates nitrogen management of the plant
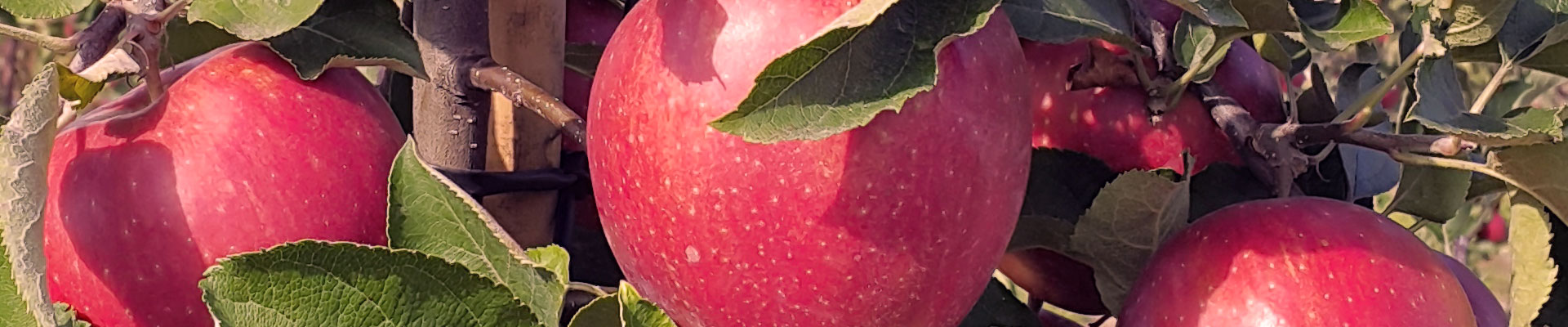
- Increases plant resistance to the occurrence of physiological and fungal diseases, e.g., with regard to apples, subcutaneous bitter spot and mealy decay
- Regulates plant resistance to mechanical damage and invasion of fungal pathogens and pests
- Coordinates the water management of the plant by regulating, together with potassium and chlorine, the daily rhythm of the stomata
- Improves the growing process and yield quality of vegetative organs and fruits
- Increases fruit firmness and dry matter and sugar content
- Reduces vulnerability of fruit to cracking and juicing (cherries, sweet cherries, strawberries)
- Improves plant condition for overwintering winter and spring stress conditions
- Extends the storage life of fruits and vegetables
- Stimulates the establishment of root papillae in faba bean plants
- Contributes to increased sugar polarization in sugar beet
- Increases the dry matter and starch content of the potato
- Improves plant vigor in the early stages of corn growth